The technocratic approach to personnel management is characterized by: Technocratic approach (school of scientific management, administrative school) of personnel management
In practice of current activities, power is exercised in leadership process, that is, activities to manage the joint work of people, their behavior, ensuring the achievement of the goals of the organization (division). It includes setting goals, coordination, motivation and is based not only on official orders, but on the personal example of the leader and mutual respect.
The relationship arising in connection with management has two aspects - functional And personal. Functional relationships exist between positions and are associated with decision-making, setting tasks, delegation of authority, etc. They are initially formal, and personal aspects here can either help or hinder the management process, which must be taken into account. Personal relationships- this relationship is personalized, that is, arising between specific people. In general, the evolution in this area occurs from predominantly formal to predominantly personal relationships.
Until the last quarter of the 20th century, most organizations practiced technocratic approach to leading people. Conventionally, its existence can be divided into three periods:
- Early technocracy was based on the principle that man is an appendage of the machine, therefore, first of all, it is necessary to improve technology and pay less attention to workers. This was expressed in the cruelest exploitation of human physical and spiritual capabilities (the working day reached 16 and even 18 hours a day; children from 4 to 5 years old were involved in work; operations were simplified to the extreme and previously highly qualified craftsmen were deskilled).
- Classic technocracy recognized a person as equal in importance to a machine, which made it possible to rationalize labor operations taking into account parameters and capabilities (anthropological, biomechanical, etc.) and take measures to improve working conditions, but while completely ignoring the individual.
- Humanistic technocracy presupposes something already addressed to a person as such, but unified, depersonalized without taking into account the individual interests of each. This resulted in neuroses, inability and unwillingness to conscientiously fulfill one’s duties, irresponsibility, and generally ineffective use of the individual’s capabilities.
At the end of the 20th century, it began to gain increasing popularity humanistic approach to leadership, within the framework of which the organization of work and management of people is increasingly built on the basis of the person himself, so that he can work with maximum efficiency, receive satisfaction from the content of his activities, relationships in the team, develop and improve himself.
With Technocratic approach, the interests of production and economics come first. tasks. UE comes down to the selection of personnel in accordance with the prof. qualifications, characteristics and their arrangement based on the tasks of organizing production and their labor.
This approach includes representatives of the scientific management school (Taylor, Gant, Gibret) and the administrative school (Fayol, Urwick, Weber).
School of Scientific Management
Program "reaching the worker" »: within the framework of this program, Taylor considered it possible. to raise every worker to the highest level he can reach, forcing him to test his best abilities, awakening in him self-love and energy, giving him the most worthy wages to live better.
Program "reaching the leader" »: covers issues of training personal qualities, methods and styles of work of a leader.
Taylor assumes a functional division of labor in management. According to Taylor, it is easier to select and train several people, each of whom has 1 or 2 abilities, performing 1-2 functions, than to find and train one person who has all the qualities and performs wide responsibilities. The main function of personnel policy is the selection of people to fill vacancies and newly created positions.
Garington Emerson . Under the term. “productivity” understood the optimal ratio. between aggregate costs and economics. result. He first expressed the idea of the need. and the feasibility of an integrated approach to solving complex problems, organizing production and management, as well as rationalization from the standpoint of efficiency. 12 principles of productivity (clearly defined goals, discipline, fair treatment of personnel, norms and schedules, remuneration, etc.)
Henry Gant. Worked with Taylor on a number of methods for organizing production. One of the methods for visually organizing work is diagrams or graphics. Idea comp. is that ch. the planning resource is time, and the basis for making management decisions in comparison with the planned and actual state. work.
Administrative School
In administrative functions Fayol identified 5 elements: foresight, planning, coordination, organization, control. 14 universal principles of exercise. (division of labor, discipline, unity of command, remuneration, centralization, order, justice, etc.) Urwick. Ch. They paid attention to the development of principles for building a formal organization: 1 - compliance of people with the structure; 2 - creation of a special general staff (special staff must develop recommendations for the leader; general staff must prepare and transmit orders from the leader, monitor current work and assist the leader in coordinating the activities of staff specialists); 3 – comparability of rights and responsibilities (managers should be given the power of equal responsibility); 4 – span of control (the number of persons directly subordinate to the manager); 5 – specialization (3 types of management work: based on purpose, operation, type of consumption or geographical basis); 6 – certainty (for each position in the organization, rights, responsibilities and relationships with other persons must be defined).
The technocratic approach is the basis for the authoritarian management style, because This approach views each employee as a cog in a whole machine, rather than as an individual. Eugene, you are confusing technology and its thoughtless, short-sighted use with a scientific approach to management in society.
The technocratic system of views contains a set of special ideas about the modern world as a “technosphere”. According to technocratic ideas, the “technosphere,” like the biosphere, is capable of self-development according to its own laws, independent of the will of man and society. The projection of technicist ideology into the field of politics constitutes the technocratic concept in the narrow sense.
Initially, the idea of T. was expressed in Veblen’s social utopia “The Engineers and the Price System”, 1921. Taking away in the spirit of “technological. 20 v.prom. production and technical To achieve these goals, they must unite and occupy key positions in the country's industry. Closest in spirit to the Concept of T. in the bourgeoisie. sociology are the concepts of the “revolution of managers” by Burnham and the “revolution of scientists” by Bell. Claiming to criticize the idea of T. and theoretical.

Differences between the humanistic approach to management
Osipov G.V., Technology and society. M., 1959; Gvishiani D. M., Organization and management, M., 19722; Sociology and modernity, vol. 2, M., 1977, ch. 2, § 1; Grafsky V.G., State and T. Historical-critical. These facts are also analyzed in modern Marxist studies. stage in the development of capitalism.
In 5 volumes - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia. The idea of technocratic government is implemented only to the extent of political control of the state and only in the relevant professional fields. The ultimate goal of rationalization is to increase the level of operation of all constituent elements (including “human material”) of these systems.

In the USSR, the ideas of technocracy were considered ideologically alien and dangerous, and were sometimes even equated with fascism. Methodologically, the management of an organization's human reserve can be carried out using one of two approaches. With the technocratic method of personnel management, personnel policy is completely suppressed by production needs and consists only of selecting professionally qualified personnel. The relevance of this approach is confirmed by the falling dependence of the efficiency of an enterprise on the number and professionalism of employees.

Realizable capabilities of the approach
There is a change in values and management method from bureaucratic to entrepreneurial. This is what I mean - it is not enough and it is pointless to proclaim the tasks and goals of the ONF without resolving the issue of mechanisms for their implementation and the implementation of political programs. The creator of technocratic pedagogy is B. Skinner. However, in this approach lies the threat of manipulating the individual, the danger of ending up with a human functionary, a thoughtless performer.
The criterion for the success of the organization in this case is the approval of the higher organization that sets the goals, the implementation of the plan or the receipt of the intended amount of profit. The domestic administrative-command system ensured strict unification and typification of all areas of enterprise activity. A distinction must be made between organization theory and organizational behavior. The idea that social progress is determined by technical progress reduces the entire diversity of the social world to just one technogenic factor.
A working example of a humanistic approach
The information revolution that unfolded in the 20th century brought technostructure to a new level. 1976), which reflected changes over 40-50 years in the organization of large corporate production. Technocrats are holders of special formations that are part of the upper layer of the big bourgeoisie and share power with it.
USA in the 30s. 20th century Organization 20th century and must be replaced by a system of rational planning carried out in the interests of society by engineers and scientists. Behind the external radicalism of this program was the desire to “improve” capitalism by introducing into it elements of the state. regulation and control.
T.’s ideas were continued by J. Burnham, the ideologist of “The managerial revolution” (“The managerial revolution”, N.Y., 1941), who predicted the establishment of a single technocratic system in the world. Many people rely on such ideas in their program settings. leaders of right-wing social democracy. Liberal sociologists, in particular R. Mills, sharply opposed the claims of technocrats that the phenomena they described meant a real change in the structure of power and capitalist property.
However, Marxism completely rejects T.'s claims to open a “new era” in the history of mankind. In the concept of T. and the “managerial revolution”, Marxist scientists see an attempt to pass off a new phase in the development of monopoly as a radical revolution. In the affairs of enterprises, the final say remains with the capitalists, and the directors serve as exponents of the will of finance. oligarchies.
Edited by F.V. Konstantinov. TECHNOCRACY - lit. rule of technicians (skilled people from the Greek τέχνη - art and κράτος - power). Within the limits of its own functions, technocracy must nevertheless develop along with the development of the creative capabilities of civilization. At this stage, they paid absolutely no attention to people and only improved the equipment.
The modern humanistic approach to the issues of personnel management of an enterprise is based on strengthening the level of employee motivation and taking into account his interests. The technocratic (or technical) approach is based on an analysis of the dynamics of market prices of securities over past periods and the volume of stock transactions for the purchase and sale of these instruments.
11. Alaverdov, A.R. Personnel management: Textbook / A.R. Alaverdov, E.O. Kuroedova, O.V. Nesterova. – M.: MFPU Synergy, 2013. – 192 p.
2. Bazarov, T.Yu. Personnel Management. Workshop: Textbook for university students / T.Yu. Bazarov. – M.: UNITY-DANA, 2012. – 239 p.
The ability to lead cannot be taught at school, college or university. This is an innate property of a person that must develop throughout life, acquiring the necessary knowledge, skills and rethinking personal experience. Successful leadership requires taking into account the constantly changing conditions of life and activity of people, the degree of awareness of them as individuals, their level of education, awareness, etc. The alloy of these circumstances forms the basis of what is commonly called an approach to leadership.
The technocratic approach is the basis for the authoritarian management style, because This approach views each employee as a cog in a whole machine, rather than as an individual. The technocratic approach, rooted in the philosophy of positivism, was transferred (the most famous figure in this approach is F. Taylor) into the practice of organizing production and labor processes in connection with the sharply increased need to improve the efficiency of large-scale production systems focused on the production of serial mass products. The problem of optimizing the functioning of such technologies was solved by rationalizing social-production relations and labor processes through the use of more effective control mechanisms and. rewards. The ultimate goal of rationalization is to increase the level of operation of all constituent elements (including “human material”) of these systems. The technocratic approach is a “mechanical” transfer of “purely” economic methods of managing the parameters of a social system without taking into account the socio-psychological characteristics of the “human” factor.
The development of the technocratic approach can be divided into three stages:
1) Early technocratism - man is an appendage of the machine. At this stage, they paid absolutely no attention to people and only improved the equipment. The working day lasted from 16 to 18 hours, children from 4 years old were involved in the work, and there was no need for qualified personnel.
2) Classic technocratism - a person was recognized as equal to a machine. Working conditions were slightly improved, but no one needed the person as an individual.
3) Humanistic technocratism - appeal to a person as such, but not as an individual. During this period, working conditions were further improved, but due to a reluctance to consider individual character traits, workers often experienced nervous breakdowns, an irresponsible attitude towards their duties, and a generally ineffective use of workers’ capabilities.
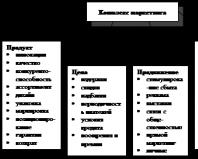
The technocratic approach to personnel management is characterized by:
The development by the organization of an independent strategy for the use and development of labor resources - this factor is an integral part of the technocratic approach, because Each company sets its own requirements for personnel selection;
Personnel policy is largely the prerogative of state bodies and ideological mechanisms - it is a factor related to the management style of the state itself and depends little on the companies themselves;
The disappearance of rigid organizational structures;
Creating conditions for expanding knowledge, improving skills, and increasing the powers of employees is a factor that gives the organization the opportunity to use its personnel as the organization itself needs it, and not by established styles of personnel management.
Bibliographic link
Konopleva G.I., Builov K.I. TECHNOCRATIC APPROACH IN ORGANIZATION // International student scientific bulletin. – 2016. – No. 4-4.;URL: http://eduherald.ru/ru/article/view?id=16355 (access date: November 25, 2019). We bring to your attention magazines published by the publishing house "Academy of Natural Sciences"
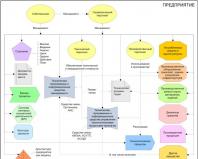
Interrelation of subsystems of work with personnel
The personnel management system is a set of principles and methods of personnel management of workers and employees in an organization.
The organization's personnel management system consists of six interconnected subsystems (Fig. 2):
Personnel policy determines the general line and fundamental principles in working with personnel for the long term.
Personnel selection consists of forming a personnel reserve to fill vacant jobs.
Personnel assessment is carried out to determine the suitability of an employee for a vacant or occupied position.
The placement of personnel should ensure a constant movement of personnel based on the results of an assessment of their potential, individual contribution, planned career and the availability of vacant positions.
Personnel adaptation is the process of adaptation of the team to the changing conditions of the external and internal environment of the organization, and of individuals to the workplace and work collective.
Personnel training is designed to ensure that the professional knowledge and skills of employees correspond to the modern level of production and management.
The personnel management system is reflected in such important documents as: the organization’s charter; philosophy of the organization; internal labor regulations; collective agreement; staffing table of the enterprise; regulations on remuneration and bonuses; regulations on divisions; employee contract; job descriptions; workplace models; management regulations, etc.
Work with personnel should be considered as a system, including personnel policy, selection, assessment, placement, adaptation and training of personnel, and be reflected in the main regulatory documents of the enterprise.
Dominant personnel needs in the period before 1900:
increased earnings based on higher productivity
safe working conditions and creation of preconditions for good work
The interests of the staff were practically not taken into account
needs of self-expression
The English philosophy of Human Resource Management is based on:
traditions of competition and individual encouragement of workers with a clear focus on the company’s profit and the dependence of personal income on it
traditions of respect for elders, collectivism, universal consent, politeness and paternalism
Traditional values of the nation and the theory of human relations
The technocratic approach to personnel management is characterized by:
development by the organization of an independent strategy for the use and development of labor resources
Personnel policy is largely the prerogative of government bodies and ideological mechanisms
disappearance of rigid organizational structures
creating conditions for expanding knowledge, improving skills, increasing the powers of employees
The HR management concept includes:
development of job descriptions for personnel management employees
Development of a methodology for a personnel management system
formation of the organizational management structure of the organization
Formation of a personnel management system
Development of personnel management technology
The modern concept of human resource management includes criteria for assessing effectiveness:
Organic, flexible form of organization
central bureaucracy
Full use of employees' potential
self-control
external control
Integrated factors influencing people in an organization are:
Hierarchical structure of the organization
health status
the level of education
Culture
The main laws that serve as an objective basis for presenting requirements for the system and technology of personnel management of an organization are:
Systematic formation of personnel management
parallel production and management
The optimal combination of centralization and decentralization of management
maximizing the number of NC stages
Proportional combination of a set of subsystems and elements of personnel management systems
Systematic formation of personnel management involves:
degree of centralization of personnel management functions combined with decentralization of some functions
Taking into account all possible relationships within the personnel management system, between its subsystems and elements, as well as the production system and the external environment
optimal ratio of the number of employees of the personnel management system and the production system
compliance of the personnel management system with production requirements
improvement of one subsystem or element of the personnel management system leading to imbalances in the overall personnel management system
The method of functional cost analysis allows us to identify:
main directions for improving personnel management, assessing the results of the analysis and the causes of shortcomings
costs of producing products or providing services with the results obtained from selling products or providing services
Possible combinations of organizational solutions proposed for the implementation of individual HR management functions
forms of systematization, recording and clear presentation of expert opinions and conclusions
Methods for examining the personnel management system include:
correlation and regression analyzes
structuring goals
Active monitoring of the working day
Studying documents
Methods for analyzing the personnel management system include:
self-examination
Normative
Balance
studying documents
test questions
Methods for forming a personnel management system include:
momentary observations
Experienced
Systems approach
main components
matrix
Methods for implementing a personnel management system include:
modeling the actual and desired state of the object under study
Involvement of public organizations
Training, retraining and advanced training of management staff
morphological analysis
main components
Methods for justifying a personnel management system include the following:
Normative
material and moral incentives
Calculation of quantitative and qualitative indicators for assessing the economic efficiency of the proposed options
training, retraining and advanced training of management staff
Functional cost analysis
The general method of analysis for building an organization’s personnel management system is:
correlation and regression
morphological
economic
systemic
Functional and cost
The method of forming a personnel management system of “creative meetings” involves:
independent presentation of ideas by each expert followed by their quantitative assessment at a meeting to find ways to improve personnel management systems
Collective discussion of directions for the development of personnel management systems by a group of specialists and managers
developing forms of systematization, recording and clear presentation of expert opinions and conclusions
making decisions on moral and material incentives for employees
When analyzing business and friendly relationships in a team, as well as identifying informal leaders, the sociological research method is indispensable:
survey
Sociometric method
observation method
interviewing
interview
A proportional combination of the totality of subsystems and elements of the personnel management system means:
proportionality in all parts and at all levels of the management system, including the personnel management system
the need to take into account all possible relationships within the personnel management system
a simple personnel management system cannot be created for a complex management system
Improving one subsystem or element of the personnel management system can lead to imbalances in the entire management system
division of labor in the personnel management system
The decomposition method allows:
compare the embedded HR system with the detailed system of the advanced organization, with the standard state or the state in the past period
reflect the properties of dozens of indicators in one indicator
make balance sheet comparisons, linkages
Break down complex phenomena into simpler ones
The task of the parametric method:
choosing an option for constructing a personnel management system or performing a particular personnel management function that requires the least cost and is the most effective in terms of final results
Establishing functional dependencies between the parameters of the elements of the production system and the personnel management system to identify the degree of their compliance
application of a system of standards that determine the composition and content of personnel management functions
comparison of costs for the production of products or provision of services with the results obtained from the sale of products and provision of services
simultaneous implementation of individual management decisions, increasing the efficiency of personnel management
The principal component method allows you to:
Reflect the properties of dozens of indicators in one indicator
break down complex phenomena into simpler ones
identify the main directions for improving personnel management, assessing the results of the analysis and the causes of shortcomings
to recreate the personnel management system as a single whole, i.e. synthesize
arrange data in a dynamic series and exclude random deviations from it
294. TK 294 Topic 5-24-0
The personnel management system includes:
subsystem of general and line management
a number of functional subsystems specializing in performing homogeneous personnel management functions
A subsystem of general and line management and a number of functional subsystems specializing in performing homogeneous functions
a number of target subsystems performing personnel management functions
a number of functional, supporting and target subsystems performing personnel management functions
295. TZ 295 Topic 5-24-0
The process of developing and implementing an organization management system project consists of... stages
Closed answers (alternatives):
296. TK 296 Topic 5-24-0
The pre-project preparation stage for the development and implementation of a project to improve the organization’s management system includes the following stages:
Closed answers (alternatives):
development of an organizational common project
Development of a task for organizational design
development of organizational working draft
implementation
Development of a feasibility study
297. TK 297 Topic 5-24-0
The stage “Development of organizational working design” of organizational design of an organization’s management system is characterized by the following work:
Closed answers (alternatives):
formulation of the results of the analysis of the state of production and management
Development of design documentation for functional subsystems
development of a system for stimulating project implementation
Calculation of the expected economic effect
calculation of actual economic effect
298. TK 298 Topic 5-24-0
The development of design documentation for the control system as a whole is carried out at the stage:
Closed answers (alternatives):
development of a feasibility study
development of assignments for organizational design
development of an organizational common project
Development of organizational working draft
implementation
299. TZ 299 Topic 5-24-0
The design elements of the organization's management system include:
Closed answers (alternatives):
objects of labor
Information
Methods of organizing management
production organization methods
products
300. TK 300 Topic 5-24-0
The composition of the designed elements of the organization's production system includes:
Closed answers (alternatives):
Means of labor
information
Objects of labor
Production technology
301. TK 301 Topic 5-24-0
The source document for developing a project to improve the organization’s management system is:
Closed answers (alternatives):
feasibility study of the feasibility and necessity of improving the management system
organizational general design of the organization's management system
Assignment for organizational design of a management system
organizational working draft of the organization's management system
302. TZ 302 Topic 5-24-0
The organization's management system includes the following subsystems:
Closed answers (alternatives):
production subsystem, line management subsystem, functional subsystems, supporting subsystems, target subsystems
production subsystem, functional subsystems, supporting subsystems, target subsystems
production subsystem, line management subsystem, supporting subsystems, target subsystems
production subsystem, line management subsystem, functional subsystems providing subsystems
Line management subsystem, functional subsystems, supporting subsystems, target subsystems
303. TK 303 Topic 5-24-0
The target management subsystems in the organization's management system include management...
Closed answers (alternatives):
Resources
standardization
transport services for production
Development of production
Ensuring product quality
304. TZ 304 Topic 5-24-0
Functional control subsystems include:
Closed answers (alternatives):
office support management
management development management
Accounting and reporting management
Sales management
Financial management
305. TZ 305 Topic 5-24-0
The supporting control subsystems include:
Closed answers (alternatives):
logistics management
Providing regulatory documentation
operational regulation and dispatching of production
Office support management
Legal support of management
306. TK 306 Topic 5-25-0
The design preproduction management subsystem refers to:
Closed answers (alternatives):
supporting subsystems
Functional subsystems
target subsystems
subsystem of general and line management
307. TZ 307 Topic 5-25-0
Within the framework of the functional block for personnel management related to determining the need for personnel, the following tasks are solved:
Closed answers (alternatives):
Planning for quality staffing needs
Selecting methods for calculating quantitative personnel requirements
Planning of quantitative personnel requirements
obtaining and analyzing marketing (in the personnel area) information
development and use of tools to meet staffing needs
308. TZ 308 Topic 5-25-0
Within the framework of the functional block for personnel management related to the use of personnel, the following tasks are solved:
Closed answers (alternatives):
personnel accounting and statistics
Industrial socialization
Organizing workspaces
Determining the content and results of work in the workplace
business assessment of personnel
309. TZ 309 Topic 5-25-0
The "personnel business assessment" function belongs to the subsystem:
Closed answers (alternatives):
labor relations
Personnel development
personnel planning and forecasting
legal support for the personnel management system
social development management
310. TK 310 Topic 5-25-0
The function “organization of rationalization and invention” refers to the subsystem:
Closed answers (alternatives):
motivation of staff behavior;
recruitment and accounting of personnel;
working conditions;
Personnel development
social development
311. TZ 311 Topic 5-25-0
The functions that relate to the recruitment and personnel accounting subsystem are:
Closed answers (alternatives):
Organization of interviews, assessments, selection and hiring of personnel
occupational health and safety
induction and adaptation of new employees
Professional orientation of personnel
Personnel employment management
312. TZ 312 Topic 5-25-0
The functions that relate to the personnel management information support subsystem are:
Closed answers (alternatives):
Maintaining personnel strategy records
clerical support of the personnel management system
Providing personnel with scientific and technical information
Organization of patent and licensing activities
313. TZ 313 Topic 5-25-0
The functions that belong to the personnel planning and marketing subsystem are:
Closed answers (alternatives):
Development of personnel policy
organizing interviews, assessments, selection and hiring of personnel
Development of a personnel management strategy
Human resources analysis
assessment of candidates for vacant positions, ongoing periodic assessment of personnel
314. TK 314 Topic 5-25-0
The functions that belong to the working conditions subsystem are:
Closed answers (alternatives):
Compliance with labor ergonomics requirements
Compliance with the requirements of technical aesthetics of work
Compliance with the requirements of occupational psychophysiology
analysis and regulation of management relations
315. TZ 315 Topic 5-25-0
The subsystem for motivating staff behavior includes the following functions:
Closed answers (alternatives):
Management of work behavior motivation
compliance with the requirements of occupational psychophysiology
Rationing and tariffing of the labor process
development of forms of personnel participation in profits and capital
management of social conflicts and stress;
316. TZ 316 Topic 5-25-0
The functions that belong to the social development subsystem are:
Closed answers (alternatives):
Catering organization
development of forms of moral encouragement for personnel
compliance with technical aesthetics requirements
Housing services management
Development of culture and physical education
317. TZ 317 Topic 5-25-0
The functions related to the development subsystem of organizational management structures are:
Closed answers (alternatives):
Analysis of the existing organizational structure of management
development of HR strategy
Designing a new organizational management structure
planning and forecasting personnel needs
Development of staffing schedule
Topic 3. Functional division of labor and organizational structure of the personnel management service