How money is paid during layoffs. How much salary is paid during layoffs?
Upon dismissal due to layoffs of citizens in accordance with the provisions of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other requirements of labor legislation, termination of the employment contract drawn up earlier is provided for. In addition, the parties have the right to draw up an agreement based on the application of the rules of Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. After this, mutual settlements between the employee and the employer are required.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 78. Termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties
An employment contract can be terminated at any time by agreement of the parties to the employment contract.
In addition, persons dismissed due to staff reduction, which is permitted by the provisions of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, have the right to claim severance pay upon dismissal due to staff reduction. These are provided in an amount proportionately calculated from the amount of previously received wages.
So, what redundancy payments are due to a dismissed employee and what compensation is due when staffing is reduced?
The employer must compensate for the period of forced downtime and adaptation when moving to a new place of work.
Consist of the following main components:
- earnings for days worked;
- compensation for missed vacation;
- additional compensation;
- benefits for the period of employment.
ATTENTION: Accruals cannot be less than one minimum wage (minimum wage) calculated for the period of time worked.
Some of these funds are issued immediately after dismissal, and some remain as a potential opportunity to receive payments in case of job reduction and compensation under appropriate accompanying circumstances, which will be discussed below.
Payments upon dismissal of an employee on the day of dismissal
The day of dismissal is considered to be the last working day, which is established by order on the basis of the provisions on staff reduction or by agreement drawn up by the parties. Regulated by the provisions of Article 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. On this day, upon request, the employee is provided with a completed work book and payment of severance pay upon dismissal due to staff reduction.
What is severance pay when an employee is laid off? Severance pay when reducing the workforce is an accrual provided only for persons officially employed by the employer - with the conclusion of an employment contract and registration of a work book. They include the amount for working days worked, allowing for the accrual of bonuses and other payments to the employee in case of staff reduction.
They add up the accrual of compensation payments when an employee is laid off for vacation days not taken off. When an employee is laid off, severance pay is paid as additional compensation or compensation for unforeseen risks during dismissal.
 Earnings for working days are always accrued, even if the employee worked as a part-time worker, seasonal worker, etc.
Earnings for working days are always accrued, even if the employee worked as a part-time worker, seasonal worker, etc.
This is an essential element of severance pay, which consists of the accrual of earnings or part of earnings commensurate with what is established in the employment contract.
When calculating it, the accountant calculates the number of working days worked but not previously paid.
Their number is multiplied by the amount of daily earnings. If the agreement of the parties specifies the payment of bonuses, they are accrued in proportion to the number of days worked.
In the absence of agreement between the parties, such an initiative may be taken by the employer, or based on previously established provisions of the employment contract or other regulations and trade union documents.
Compensation for unused vacation is accrual made in favor of permanent employees for whom the provisions of labor legislation provide for annual leave. Their size depends on:
- number of days off;
- average earnings.
The number of days presented for payment depends on the number of months that have passed since the completion of the previous vacation and the length of the vacation period. For example, a specialist is entitled to 24 working days of vacation - this amounts to 2 calendar days, accumulating in each month.
Accordingly, if the dismissal took place 8 months after the specialist returned from vacation, he is entitled to pay 16 working days in the form of the indicated compensation.
Additional compensation is accruals that are issued to persons who draw up an agreement to terminate an employment contract. Their scope is regulated by the provisions of the agreement or at the discretion of the employer.
IMPORTANT: The employer can provide additional compensation when reducing the number or staff of employees, but is not obliged to do so. Accordingly, the person resigning has no right to claim this type of payment.
Additional compensation payments when an employee is laid off can be paid either as a lump sum or in installments, in a manner convenient for the parties. The amount must be precisely defined in the terms of the agreement.
 Average earnings for the period of employment - these accruals are provided for in all cases when, at the initiative of the employer, a person who conscientiously performs functional duties is dismissed.
Average earnings for the period of employment - these accruals are provided for in all cases when, at the initiative of the employer, a person who conscientiously performs functional duties is dismissed.
As the average earnings, the proportionate earnings for the last year are used, from which payments received under social insurance are deducted - for being on sick leave, on maternity leave, etc.
If, as a result of calculating average earnings, it turns out to be lower than the minimum wage provided for by law, it should be raised to the established minimum amount.
The average earnings received are calculated in the amount of working days calculated over two months. At the discretion of the employer, if the dismissed person was previously accrued a fixed salary, two months' salary may be issued.
Contributions and taxes. In Labor legislation, when citizens are dismissed due to staff reduction, the provisions of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation come into force, which repeal the force of Articles 208, 212 of the Tax Code.
That is, tax withholding is not made in this case. However, Article 178 establishes restrictions on the amount of payments upon dismissal due to staff reduction, and the remaining funds exceeding the established standards are taxed in the general manner.
In established cases, contributions to the Social Insurance and Pension funds are deducted from the average daily earnings and vacation pay compensation.
In what cases is the benefit accrued for the second month?
Sometimes an employment contract or collective labor agreement, as well as other regulatory acts of personnel production, provide for the accrual of benefits in the second month after dismissal. For the second month, compensation payments for dismissal due to staff reduction are provided to the dismissed person as financial support for the period of prolonged adaptation after the reduction.
 Such a legal precedent is permissible within the framework of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The benefit is paid only if an employee dismissed due to staff reduction was unable to find a job due to objective circumstances beyond his control.
Such a legal precedent is permissible within the framework of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The benefit is paid only if an employee dismissed due to staff reduction was unable to find a job due to objective circumstances beyond his control.
These accruals are made from the employer's budget, in the amount of the average monthly salary or basic earnings. It is allowed to calculate the average daily earnings, without accrual of bonuses and minus the payment of insurance benefits, but not less than the minimum wage.
Additional payments in case of staff reduction for the second month are provided regardless of the fact that the dismissed person has already received compensation in the amount of two months' salary (average earnings).
Here it is also possible to receive additional compensation if it was provided for by agreement of the parties and postponed to the second month.
How to receive payment for the third month?
If an employee dismissed due to staff reduction was unable to find a job within two months, then the third month can also be paid. In this case, it is impossible to demand mandatory payment by the employer for forced absence.
This will require an official application from the Employment Service. For persons who are not registered with the local branch of the Employment Service, such benefits are not provided..
What does an employee have to do in case of staff reduction? After submitting a formal petition, submitted to the former employer and attached to the handwritten application, the employer accrues the last payment provided as severance pay for the employee dismissed by him.
Its volume is also based on the average monthly earnings provided for the second month of forced unemployment.
REFERENCE: If the recipient of the benefit was employed within a month, then payment is allowed when reducing only the period (number of days) when he was not employed.
More detailed information about severance pay in case of staff reduction is presented in this video:
Unemployment benefit
In the subsequent period, a citizen who is not employed due to redundancy applies for unemployment benefits.
 To do this, you need to register with the local employment service office, write an application and attach documentation:
To do this, you need to register with the local employment service office, write an application and attach documentation:
- passport;
- diploma, certificates and other documents on education (qualifications);
- certificate of average earnings from a former employer;
- work book.
The benefit is accrued after registering as an unemployed person on the employment exchange., but not earlier than the day before which the unemployed receives benefits and other compensation from the employer.
The amount provided for payment as a benefit to the unemployed is provided by decision of the administrative commission, in amounts from 850 rubles to 4,900 rubles. Payments are calculated from the regional budget, so a regional coefficient may be added to the basic amounts.
The duration of benefit payment is based on objective reasons and is carried out:
- until official employment through the exchange or through independent searches.
- If a citizen cannot find a job despite the conscientious actions of the SZ inspectors - until the moment of three times unjustified refusal of a suitable job provided to him.
- If a citizen does not appear to the inspector supervising him without warning of a valid reason within a month.
- Before going on maternity leave, when the payment of social benefits begins.
- Until you receive other subsidies and benefits that can be considered as income. Including old age or disability pensions.
- Before being called up for military service.
REFERENCE: Full-time students who do not receive a scholarship do not receive unemployment benefits.
What determines the amount of each benefit?
 The amount of payments due when an employee is laid off depends on the following related reasons affecting the accrued amount:
The amount of payments due when an employee is laid off depends on the following related reasons affecting the accrued amount:
- salary (other income);
- the number of days allocated as vacation pay;
- payment provisions included in the agreement;
- employer's decision.
In the second and third months, the benefit amount is based only on average earnings (salary).
The employment exchange calculates benefits based on various nuances. Persons laid off due to staff reduction who registered as unemployed in a timely manner may qualify for the maximum benefit amount.
What to do if the employer does not pay compensation for staff reduction?
The procedure for paying compensation during layoffs is regulated by the provisions of Article 13 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The calculation and issuance of the required severance pay is provided to citizens on the last working day, which is considered the day of dismissal.
This procedure is supplemented by Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which allows the issuance of settlement benefits later, but for reasons of valid absence of the dismissed person on the day appointed for issue.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 140. Payment terms upon dismissal
Upon termination of the employment contract, payment of all amounts due to the employee from the employer is made on the day the employee is dismissed. If the employee did not work on the day of dismissal, then the corresponding amounts must be paid no later than the next day after the dismissed employee submits a request for payment.
In the event of a dispute about the amount of amounts due to the employee upon dismissal, the employer is obliged to pay the amount not disputed by him within the period specified in this article.
ATTENTION: The absence of an employee from the workplace on the day of dismissal without a valid reason allows for the imposition of a disciplinary sanction, with a review of the grounds for dismissal.
Any violation of the established regulations by the employer is considered a violation of labor legislation. These actions are mainly divided into two types:
- violation of delivery deadlines;
- arrears during accrual.
The following authorities are responsible for protecting the civil property rights of employees, which can intervene in the unfair actions of the employer. Among them:
- trade union;
- State Labor Inspectorate (STI);
- prosecutor's office;
- arbitration or civil (general jurisdiction) court.
 In case of arrears during accrual, the employee is required to receive the accrued amount in his hands, and for the remaining (claim) amount to submit a notification claim to the manager, with a warning of the intention to appeal.
In case of arrears during accrual, the employee is required to receive the accrued amount in his hands, and for the remaining (claim) amount to submit a notification claim to the manager, with a warning of the intention to appeal.
If the payment is not issued on the last working day, it is permissible to submit a notification at the end of the working day, also addressed to the head of the organization.
At the same time, you can contact the trade union organization at your place of work by writing a statement about violation of labor rights addressed to the chairman.
IMPORTANT: Submitted notification documents must be registered by a specialist in the general department or submitted against signature, which is affixed by an authorized official on the second copy.
If the applicant does not receive an immediate response, with a certificate from the manager about the restoration of his violated rights, the next day he can file a complaint with the State Tax Inspectorate. If the employer’s dishonest actions do not stop, it is permissible to contact the prosecutor’s office.
In another case, when the employer has set a deadline for restoring the violated rights of the employee, but has not corrected the violation, it is advisable to file simultaneous complaints to the State Tax Inspectorate and the prosecutor’s office.
Going to court is a last resort measure, which is used after preliminary attempts to resolve the issue out of court. You can go to court:
- if consideration of the complaint by the State Tax Inspectorate and the prosecutor's office is rejected, within 10 days after receiving a reasoned refusal.
- If these authorities did not find any violations, then within 10 days after receiving an extract from the decision of the inspector or prosecutor’s inspection.
The statement of claim is written in the form established by 131 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. It is submitted at the place of legal address of the defendant, who will be the employer (Article 35 of the Arbitration Procedure Code, 28 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, Article 35. Filing a claim at the location or place of residence of the defendant
The claim is brought to the arbitration court of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation at the location or place of residence of the defendant.
Article 28. Filing a claim at the place of residence or location of the defendant
The claim is brought to the court at the place of residence of the defendant. A claim against an organization is filed in court at the location of the organization.
In certain cases, the material is transferred to the court by a GTI inspector or prosecutor.
Employer's liability
 Based on Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the head of the company, based on the results of an inspector and prosecutor's audit, may be subject to penalties, including recording them in his personal file.
Based on Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the head of the company, based on the results of an inspector and prosecutor's audit, may be subject to penalties, including recording them in his personal file.
In addition, an unscrupulous attitude towards the performance of functional duties, leading to a violation of the rights of members of the workforce, leads to the imposition of penalties.
The fines vary.
In case of malicious violation of workers' rights, on the basis of abuse of official duties, criminal liability may be imposed.
In this case, the official guilty of violations may, by a court decision, not only pay a fine, but also receive restrictions on the management of the organization.
All fines and other types of punishment imposed on the employer do not cancel the responsibility to pay the required severance pay to the employee.
Incorrect (downwards) accrual of benefits or failure to provide them in a timely manner are considered dishonest actions of the employer and require assertion of one’s legal rights.
The article contains the main provisions that will help determine the amount of severance pay due.
This method of terminating an employment contract stands out among others. It can rightfully be called one of the most protective rights of the employee, not the employer. Although this option is the most labor-intensive.
What the law says
Clearly articulating the differences between reduction in numbers And staff reduction the law does not.
In practice, there is only one difference: when reducing numbers, a position is not excluded from the staffing table, only the number of people occupying it changes (there were 5 managers, 2 will remain).
And if the staff is reduced, then the position is removed from the schedule altogether (for example, the position of a materials accountant is excluded, his duties will be performed by a payroll accountant).
Making changes to the staffing table
It is possible to reduce employees only when the position is no longer on the staffing table. Thus, you can make changes to an existing schedule, or develop another one, taking into account all the changes.
The new version of the schedule is approved by the relevant order, which also explains why the need for reduction arose and when it will be carried out.
All employees of the company or enterprise must be familiar with this order.
Categories of persons who cannot be reduced
Reduction in the number of employees or staff - This is entirely an initiative of the management of a company or enterprise. At the same time, there are benefits for certain categories of employees. This will be discussed in more detail below.
In general, during layoffs, a certain rule applies, which is reflected in the law: those employees who have less qualifications and low labor efficiency indicators are fired first. In practice, these are most often employees with the least work experience.
The following employees enjoy the advantage of remaining at work:
- Are parents of disabled children;
- Single mothers;
- Single fathers;
- Are the sole breadwinners in the family;
- Injured or prof. diseases in this particular workplace;
- Persons who became disabled in wars;
- Heroes of Russia and the Soviet Union;
- Victims of the Chernobyl disaster;
- Victims of tests in Semipalatinsk;
- Those undergoing training for which they were directed by the organization;
- Employees who patented inventions (USSR legislation applies here);
- Heads of trade union organizations;
- Representatives of the team elected by voting who take part in resolving conflict situations with management.
So, it is unacceptable to dismiss due to reduction:
- Persons, ;
- An employee who has a sick leave certificate;
- Women who have children under 3 years of age.
This list is not exhaustive; the full list is given in the legislation.
Reasons for laying off employees
The law does not directly establish reasons for dismissal due to redundancy. It is the employer's right to make a reduction if economic conditions arise that require it. But if a dispute arises, the court has the right to check how compelling the reasons were and whether the reduction was justified.
Generally, serious circumstances include:
- Inability to pay wages to a large staff of workers;
- There are positions on staff that are not currently required;
- Production technology is changing, and therefore some employees will not be in demand.
Conditions for dismissal
Their compliance primarily concerns the employer if he does not want to pay fines and compensation to illegally dismissed employees in the future.
- The downsizing procedure must be strictly followed. Any deviation from it will entail a lot of negative consequences;
- The dismissal must be justified, and the court has the right to verify this;
- The employment service must be notified. Employers who ignore this condition often have to pay fired employees for forced absences, already by court decision.
Order and procedure for reduction
Dismissal due to reduction is carried out in the following order:
- The company's management issues an order indicating planned reductions. And no less than 2 months before the dismissal of employees. Each employee is warned about this personally, and gets acquainted with the order upon signature;
- Employees subject to layoffs must be offered other positions that correspond to their qualifications. It is worth considering that this is done not just once, but throughout the entire period before termination;
- The trade union organization must be notified if it operates in the company. If there is a massive layoff, then notice of layoff sent to the trade union 3 months in advance, as required by the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation in its determination;
- In addition to the trade union organization, the employer also warns the employment service;
- If an employee does not agree to any of the proposed vacancies, an order to reduce staff is issued. The employee’s refusal must be in writing and signed by the employee;
- With the consent of the employee, he may be dismissed before the expiration of the two-month period.
Employee rights when staffing is reduced
Many people are poorly versed in the laws, which sometimes becomes convenient for unscrupulous employers. Taking advantage of this situation, they often violate the rights of employees and do not make all the required payments. To prevent this from happening, it is worth considering this point in more detail.
What does an employee have the right to, guaranteed by law:
- Severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings;
- To maintain this income until you find a new job (a time limit has been set);
- For compensation provided for in an employment or collective agreement.
From the above examples it is clear that the state protects citizens from layoffs at the whim of management and provides the opportunity to challenge dismissal in court if it is illegal.
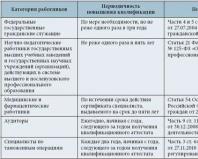
How are payments made upon dismissal due to staff reduction?
Table 1. Payment procedure
What to do if payments have not been made in full
Important information : any delay in payments is a violation of the law!
If this order has been violated, any employee can go to court, demanding:
- Compensation for vacation that was not used;
- For sick leave that was not paid;
- For moral experiences;
- Compensation for expenses incurred when contacting a lawyer;
- All % due for delayed payments.
At the same time, you can contact the prosecutor's office. Usually frightened employers pay everything. If this happens, you can drop your claim.
The statute of limitations for filing a complaint with these authorities is 3 months from the date of dismissal.
In any case, you need to carefully study your rights and learn how to protect them.
How to resign more profitably: by layoff or by agreement of the parties
Let's conduct a small comparative analysis of the two types of dismissal. Since employees quite often ask specialists this question, it is worth paying attention to its consideration. And we will present the results in the form of a table.
table 2.Comparative analysis of types of dismissal
How profitable it is to quit is up to everyone to decide for themselves. You can rely on the criteria given in the table, or you can ignore them. In any case, you need to focus on the situation that has developed for a particular person.
Employer mistakes
- Pressure on an employee to force him to resign of his own free will. Usually dictated by a reluctance to make payments required by law;
- Dismissal of an employee who is included in a preferential category (the categories are discussed above);
- Lack of coordination of the reduction procedure with the trade union (if there is one);
- Reduction without written notice.
This list contains the most typical and common errors. Some of them are interpreted by the legislator as illegal dismissal and carry serious legal consequences for the irresponsible employer.
Conclusion
To summarize, we can say that dismissal due to staff reduction can affect any person. No one is immune from this, especially if there is a difficult economic situation nationwide.
In such a situation, it is important to know your rights and ensure that they are not violated. And if certain difficulties arise, seek help from competent specialists.
In modern economic conditions, more and more companies are forced to resort to layoffs of their employees and provide them with appropriate payments. In order to be prepared for such a step in advance, you should know what guarantees are approved by law and how to correctly calculate the entire amount due - more on that right now.
Any procedures in labor relations are prescribed in detail in the Labor Code and other regulatory documents. In particular, all issues related to staff reduction are considered in Articles 81, 178, 179 and 180 of the Labor Code.
This procedure involves drawing up documents at each stage:

In parallel with this document, representatives of the personnel service must send a notification to the Trade Union, in which they indicate a complete list of those being laid off, regardless of their membership in this organization. Often, the employer sends a written notification to the employment service - such a measure is mandatory if a massive reduction in staff is expected.
- Finally, the actual dismissal based on the reduction of company employees (a corresponding order is issued and the required payments are made).

The HR department representative makes an appropriate entry in the work book.

NOTE. The employer must offer the laid-off employee similar or other vacancies (if available) at his enterprise or its division until the day of dismissal. Thus, inviting third parties to fill any vacancies is a violation of the rights of the employee, who can decide to transfer to a new position right up to the day of his layoff.
Payments upon layoff
All payments can be divided into 2 large groups:
- Those that are issued as a lump sum upon dismissal.
- Those that are paid additionally if the citizen is unable to officially find employment within a predetermined period.
Payments upon dismissal
As with any dismissal, a full settlement must be made with the employee on the last official day. However, since the dismissal occurs due to its reduction, the complete list of all types of payments will be as follows:
- salary for all days worked along with all mandatory payments - bonuses, additional payments for length of service, regional coefficient, etc.;
- payment for all vacation days that the employee did not use - all unused days that arose over the last 2 years are taken into account; ;
- severance pay – it is the amount of the average salary for one month.
All these funds must be credited to the employee’s account on the last day of work along with his work book.
NOTE. Even if an employee immediately gets another job, he must still receive severance pay. Subsequent payments depend on employment.
Subsequent payments
In the subsequent period, the employee has the right to receive an average salary for 2 months, if he still has not found an official job. In some cases, the former employer must pay the average salary for 3 months:
- the citizen officially registered with the local state employment service no later than 14 calendar days from the date on which the layoff occurred;
- the citizen regularly fulfills all the requirements of the employment service (job offers, interviews);
- Moreover, even after 3 months, the former employee did not find a new job, and the employment service decided to keep his previous salary - the decision about this is documented.
Another guarantee for the employee after his layoff is that he can receive all due sick leave payments within 1 month from the date of layoff. It does not matter when this sheet was opened: during work or after the fact of dismissal.
Thus, an employee’s ability to receive payments due to layoffs depends on the period during which he will not be employed:
- For 1 month, the employee enjoys the same opportunities as during official employment(salary and sick leave). Similar guarantees also apply to cases where an employee has retired due to old age.
- Within 2 months, he is guaranteed to receive a salary (if he is not officially employed), but will not receive payment for possible sick leave.
- Within 3 months, he will receive a salary only if he is timely registered with the employment service and does not have a new official job.
- For 4 and subsequent months, a citizen can only count on receiving unemployment benefits and social benefits (if the income for each family member is less than the subsistence level for the corresponding category of citizens - children, able-bodied people and old-age pensioners). Those. starting from 4 months after the date of dismissal, the employer does not have any obligations to the former employee.

NOTE. If, after receiving notice of dismissal, the employee has shown an intention to resign at will, and there is more than 2 months left before dismissal, then he will still receive compensation. It will be calculated based on his average salary, and the payment will be based specifically on the number of working days that remain before the start of the 2-month period before the expected layoff.
You can learn more about what rights an employee has in a layoff situation here.
How to receive redundancy payments
Payments that the employer is obliged to credit to the employee’s account on the last day of work (salary, severance pay, compensation for unused vacation days) are made automatically, i.e. without making any additional statements. All other payments to an employee upon layoff are not “automatic” - i.e. the citizen himself must ensure that the former employer accrues them.
Thus, in order to receive funds, after the first month, the former employee must contact the employer personally or through a representative (by proxy) and provide the following documents:
- application (drawn up in any form);
- passport;
- employment history.
In case of need to pay for sick leave, the original of this document is also provided. And if we are talking about payment after 3 months of unemployment, then the employee additionally provides documents that confirm the fact of his registration with the employment service.
NOTE. The text of the collective labor agreement and/or the employer’s local act may contain reference to a different procedure for paying severance pay. For example, it may be higher than the average salary and paid over six months. Therefore, before dismissal, you should pay special attention to these documents. In any case, they should not contradict labor laws.
How to calculate severance pay
Since in a situation where an employee is laid off, there are clear rules for calculating payments to him, you only need to focus on 2 key conditions:
- Average employee earnings.
- Reduction date.
As already indicated, the date of reduction must be provided by the employer in the relevant documents:
- Order on the proposed reduction.
- Order of dismissal due to reduction.
- Work book.
- All salary accruals for the last 12 months. This should include all payments, except sick leave and vacations, as well as possible compensation that is not related to salary -.
- The number of days actually worked (again, excluding vacation and sick leave).
The first value should be divided by the second - this will be the guideline for calculating severance pay (it should be no less than the average salary). More details can be seen here.
Who gets hired first?
Most often, we are not talking about mass layoffs, but about the partial reduction of some positions, therefore the question arises as to which employee has a priority right to continue working. This problem is especially relevant for large companies in which there are a number of similar positions.
In such a situation, the following circumstances are taken into account:
- Pregnant women and women with a child who is currently less than 3 years old cannot be fired.
- Next, the standard rule is taken into account - employees with higher qualifications and/or labor productivity indicators are retained.
- If several employees have the same qualifications and performance, then according to the standard rule the final decision remains with authorized persons, but they must give preference to the following categories:
- employees who have 2 or more dependents;
- employees who have no other relatives in the family with permanent work and income;
- employees who, during any period of work at a given place, acquired an occupational disease or suffered an accident in connection with the performance of professional activities;
- disabled people of the Second World War;
- employees who are currently improving their qualifications at the request and official direction of the employer.
Practice shows that challenging a preemptive right is quite successful only in the case of a clear violation (when the employee belongs to one of the above categories). Proving a higher level of qualifications, work quality indicators and labor productivity is a more ambiguous procedure.
Payment of 13 salaries
In labor legislation, the concept of 13 salary is not directly reflected. However, in practice, this phenomenon still exists, and the procedure for its payment is prescribed in the company’s internal documents:
- employment contract with the employee;
- collective labor agreement;
- local acts.
They are the ones that need to be carefully studied in a situation of possible or ongoing staff reduction. The main thing is what you need to pay attention to whether the payment for the 13th salary refers to the actual salary.
Payments in case of staff reduction often turns out to be a problem for everyone involved in the situation. It is accompanied by many nuances and not the simplest legislative regulation. To avoid all sorts of mistakes, it is worth knowing how it is calculated and in what order it is issued.
How is the payment of severance pay regulated when staffing is reduced?
This procedure is administered by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which determines that:
- all citizens have the rights to decent wages;
- in the event of liquidation of the company, reduction in the number of personnel, or resignation at will, employees can count on money from the employing organization.
This payment is severance pay in case of layoff. By law, it is accrued or issued to the employee on the last day of his work at the enterprise. Consequently, the issue of the timing of receiving funds has already been resolved.
This money is provided by law with the purpose of helping a person in the process of finding a new job, giving him the means to live for a certain period of time. What severance pay is accrued upon layoffs depends on the type of termination of the employment contract. But, as a rule, this is full payment for the first month and partial payment for the second and third after the employee leaves.
If an enterprise eliminates some positions, it is impossible to immediately say whether the laid-off workers will have to be given an average monthly amount to support them while looking for another job, and what its exact amount will be. Therefore, first we will consider a simple and mandatory procedure for calculating benefits.
The organization must pay the average monthly income to the employee, guided by Part 1 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
To receive such severance pay upon layoff, the employee does not even need additional papers; it is important to indicate the correct reason for the break in relations in the order and be sure to refer to the corresponding paragraph in the legislation. Part 1 of Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation sets the final date for the reduction as the deadline for issuing money. If a person does not appear on this day, he must submit an application, according to which he will be calculated no later than the next day after the date of application.
There are situations when a worker is not satisfied with the amount of severance pay during a layoff. In this case, the company will have to give out an amount when calculating that no one will doubt (refer to Part 2 of Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If you do not have time to transfer the funds, then the delay is fraught with interest accrual, which will grow daily, including the date of actual disbursement of money. Interest is calculated based on 1/300 of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Procedure for payments in case of staff reduction
The Labor Code in the first and second parts of Article 81 indicates that when staffing is reduced, material compensation is assumed in the form of social compensation to former employees. Let's name the main types of these payments.
- Severance pay in case of staff reduction in the amount of the average monthly earnings of the dismissed employee. If the employment agreement or any collective agreement contains information about increasing the amount of “compensation”, the employer will have to comply with the agreements and calculate the severance pay in accordance with this document.
- Maintaining average earnings for the period of employment, but no more than two months from the date of dismissal. In order to comply with the requirements of the first part of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which regulates labor relations, in this situation, when calculating the amount of average income, the amount of redundancy benefits is taken into account.
The second part of the same article indicates the possibility of a dismissed employee to insure against lack of money in case he fails to get a new job within the next two months. To do this, he should contact the employment service no later than 14 calendar days after the date indicated in the order to reduce the number of personnel. If a person has not found a new place in two months, and the employment center was also unable to offer him a job, then for the next 30 days the average income will remain with him in the form of severance pay in the event of a reduction.
Sometimes the amount of compensation is even greater than in the example considered. Some conditions require the payment of large “compensation” upon dismissal of an employee.
There is a general rule fixing the employer’s obligation to notify staff of an upcoming dismissal at least two months before this event (a sample notification document can be found below). If one of the employees decides to leave before the specified date, then he has the right to severance pay and compensation in the amount of average monthly income, recalculated in accordance with the remaining time until the stated day of reduction. Such premature termination of the contract must be formalized in writing.
The funds that are due to the employee while searching for a new job are not wages, so the company is not obliged to transfer them on the same days that are defined by local documents as the dates for issuing advances and salaries to the organization’s employees. These benefits can be transferred to a person at the end of the second and third months on dates approved jointly with him.
Calculation of severance pay in case of staff reduction
How is severance pay paid to employees in the Far North?
Special financial conditions are provided for citizens working in the Far North. Firstly, if an employee is laid off, severance pay is guaranteed to him for one quarter if he did not go to the employment center (Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 318), and for six months if he registered in the next 30 days after termination agreement.
How is severance pay paid to seasonal workers?
Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that seasonal employees are entitled to compensation in the amount of two weeks of work. The enterprise is not obliged to pay in any way for further time away from employment.
Is it necessary to pay severance pay when laying off an employee who is on a probationary period?
Despite the fact that an employee on a probationary period is not yet fully part of the company, he can claim all the compensation due to the dismissal of permanent employees.
But if an enterprise reduces it under Article 71 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the person is recognized as having failed the test and does not receive any benefits or compensation.
Is a pensioner entitled to severance pay during a layoff?
The legislation does not establish any differences between elderly and other employees who have been laid off, so the rights of the former do not change in any way, and they are also entitled to financial compensation.
Answers to related questions are contained in the chapter “Guarantees and compensation for employees who are faced with termination of their employment contract.” The situation is regulated by its articles 178-181, which do not contain any clarifications regarding special conditions for workers of retirement age.
Who is entitled to severance pay due to a fourfold reduction?
There are a number of specialists who are entitled to larger compensation in the event of a breakdown in their employment relationship. People in the civil service can count on four times their average monthly income upon dismissal, and judges can count on six times.
In what amount should severance pay be paid to part-time employees when they are laid off?
Persons working part-time, in accordance with the law and other regulations, have the same rights to financial assistance and guarantees as permanent employees. Consequently, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the same payment procedure for them as for everyone.
If a part-time worker is subject to a reduction in the number of employees or staff, the employer is obliged to pay him compensation under Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - the average income of a dismissed person for one month.
- Dismissal by transfer: rules of procedure
How to calculate severance pay when reducing staff
The first thing that management must take into account is that the salary of the dismissed employee for the last month should not change or be calculated according to some other principle. No raises or additional benefits can be canceled due to the fact that the company does not see the value in this person.
For example, money for unused vacation days must be calculated in the manner established by the fourth part of Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and paragraphs 10-12 of the Regulations on Average Earnings.
Severance pay for layoffs includes compensation for unused vacation, accrued in proportion to calendar days. However, in order to determine the number of days for which payment is due, you need to take into account the following feature.
If the employment relationship is terminated in accordance with paragraph 2 of part 1 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and the employee spent more than a year at the enterprise, then for the final working year he receives compensation in full, provided that the length of service that determines the right to paid leave is 5, 5 months or more (this point is clarified by the Rules on regular and additional leaves).
Severance pay for layoffs according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is the salary of the dismissed person in the amount of the average monthly salary. This payment is calculated in the manner established by the 3rd part of Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the 9th paragraph of the Regulations on Average Earnings. The general rule is this: it is necessary to determine the average wage per day of work by dividing the accrued wages over a certain period of time by the days actually worked during this period. At the same time, Article 178 (1st part) of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that the calculation must be made based on the number of working days that would be on the employee’s schedule in the month following the date of dismissal.
There are cases when an enterprise uses summarized recording of working hours, which affects how severance pay is calculated in the event of a layoff. In this case, the person will receive compensation for the number of working hours that will not be worked due to dismissal. The number of hours is determined based on a fixed working week (most often 40 hours).
The legislation gives citizens the right to receive their average income while looking for a new job. This period begins on the date following the day of dismissal and ends on the day before employment or after payment of severance pay for the second month upon reduction, if this moment came earlier (Article 14 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The first month of the employment period is paid on the day of the layoff, so the money for the next month is calculated taking into account the benefits (according to Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
How to calculate compensation for staff reduction: example
Let’s imagine that proofreader Ilya Kubikov got a job at OiTv LLC on December 3, 2012. A year and a half later, the company decided to reduce the personnel of the enterprise, and on April 30, 2014, Ilya was given a notice stating the severance of labor relations from July 11 of the same year (according to the first part of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). To calculate what severance pay an employee is entitled to during layoff, you need to clarify his working conditions.
Kubikov corrected texts in the company during a 40-hour work week and rested on Saturday and Sunday. In the year preceding his dismissal, Ilya had a salary of 40 thousand rubles and a bonus for qualifications, paid every month, in the amount of 5.5 thousand rubles. And on January 1, 2014, OyTv LLC increased the wages of all employees, and the proofreader began to receive 45 thousand rubles. The company applied the rules of the Regulation on Bonuses, which states that the monthly bonus is equal to 0.1 of the amount actually paid for working hours in the current period. So in April 2014, Ilya received an annual bonus in the amount of 40 thousand rubles (however, it was calculated without taking into account the employee’s actual working time). The system of material incentives at OiTV included New Year's gifts, so at the end of 2013. Ilya was paid another 2,000 rubles in honor of the upcoming holidays.
To complement the example of calculating severance pay during layoffs, it is important to note the employee’s sick and vacation days.
Ilya Kubikov was ill for nine calendar days from 01.07.2013 to 30.06.2014 (from 5 to 13 November) and took three vacations:
- Kubikov took 28 days of paid annual leave (December 2-29, 2013) and four more days on August 5-8, 2014. In 2014, the employee was accrued 7,994.4 rubles in vacation pay, and in April of the same year, personal income tax was transferred from it .
- Ilya spent two days (December 30-31, 2013) on unpaid leave.
After an employee is laid off, severance pay must be calculated taking into account all these nuances.
Ilya went to the employment center immediately after his dismissal from the OyTV company, but they could not find him a job until the end of the third month after layoffs at the company. When the second and third months of searching for a new job were up, Kubikov came to the company with all the required documents in order to receive the necessary payments.
In order not to get confused, let's turn to the schedule, which reflects everything that happens in the period between the notification of future dismissal and the final payment of severance pay upon layoff to Ilya Kubikov.

1. We calculate wages for hours worked in the month of dismissal. Proofreader Kubikov was fired on July 11, 2014, which means he is entitled to the following payments on the day of termination of the contract:
- Salary for days worked in July: 45 thousand rubles / 23 working days in a month × 9 days actually worked in July = 17,608.7 rubles.
- The fixed bonus for the qualifications of a proofreader, assigned to him earlier, is 5.5 thousand rubles.
- Estimated monthly bonus: 17,608.7 rubles salary × 0.1 = 1,760.87 rubles.
We sum up all the indicated amounts and get Ilya’s income in July: 24,869.57 rubles.
2. We will calculate the amount of compensation for unused vacation in order to include it in the severance pay in the event of a layoff.
To determine the amount of benefits for vacation days that the employee did not use, it is first necessary to calculate the average amount of earnings for one day.
The billing period from July 1, 2013 to June 30, 2014 was not fully worked out by Kubikov.
The amount of payments taken into account. Since during the time period taken for calculation, OiTv LLC increased staff salaries, the increase coefficient will require adjustment, otherwise an error will be made in our calculations.
Let's calculate the increase factor. To do this, you need to divide the new amount of salary and bonus by the old one: (45 thousand rubles + 4.5 thousand rubles) / (40 thousand rubles + 4 thousand rubles) = 1.125.
The coefficient (let’s call it k) for 2014 is equal to 1, we do not take into account the 5,500 ruble bonus in accordance with paragraph 16 of the Regulations on Average Earnings. Calculations of the amounts that will be used in compensation for severance pay in case of reduction are reflected in the following table:

Thus, we see that 582,753.95 rubles is the amount of all cash payments to Ilya for the year (we do not take into account the bonus).
Annual bonus amount. In 2013, this type of incentive was given to Kubikov in full, but without taking into account the actual work time.
Although Ilya Kubikov was officially employed by OiTv LLC throughout 2013, the billing period in which the bonus money was transferred to him was not fully worked out. So it is necessary to recalculate the amount of annual remuneration based on the days actually worked in the company.
During the specified period of time, there were only 248 working days, of which Ilya worked 215. Therefore, the amount of the bonus for the year, which will be used in calculating compensation for unused vacation, will be: 40 thousand rubles / 248 days × 215 = 34,677.42 rubles .
Unaccounted payments. The amount of severance pay in case of reduction based on the third and fifth points of the Regulations on average earnings is not affected by:
- Funds paid for vacation.
- Compensation in case of temporary disability.
- New Year's gift from the company.
We sum up all of Kubikov’s annual income taken into account and get: 34,677.42 rubles + 582,753.95 rubles = 617,431.37 rubles.
The next step in determining the average income of an OiTv employee per day is to count the number of calendar days. Their number in partial months (when Ilya went on vacation or rested during the holidays) is:
- 20.51 days in November 2013 (calculation example: 29.3 / 30 days of the month × (30 days – 9 days));
- 0.95 days in December of the same year (29.3 / 31 days × (31 days of the month - 30 days of vacation));
- 25.52 calendar days in May 2014 (we calculate as follows: 29.3 / 31 × (31 – 4 days)).
When determining the amount of severance pay when reducing the proofreader Kubikov, we will operate with a number of days equal to 310.68 (9 full working months × 29.3 + 3 incomplete).
Average daily earnings. We divide the employee’s recorded income in the billing period by the number of days worked: 617,431.37 rubles / 310.68 = 1,987.35 rubles. We received the cost of one working day for Ilya.
Ilya Kubikov fully worked the first year after his employment and used up his entire annual leave, going on vacation for 28 days in December 2013.
In this example of calculating severance pay for layoffs, the employee was fired before the end of his second year of work in the company. Since the year was interrupted on July 11, 2014, and not on December 2, 2014, as per the employment contract, Ilya’s vacation experience at OyTv LLC was ultimately 1 year, 7 months and 9 days.
According to the Leave Rules, when calculating work periods, periods of service lasting less than half a month are not taken into account in the benefit. Since Kubikov took a year off and we took nine days off, compensation will be paid based on seven months of service. But this is more than 5.5 months in accordance with Part 3 of Article 28 of the Vacation Rules, so Ilya is entitled to the amount for the whole year.
But during these seven months, Kubikov went on vacation for four days, so that if he was laid off, money for 24 unused days of rest would be added to his severance pay. We multiply the cost of a working day (average) by 24 calendar days and get the amount of compensation:
1,987.35 rubles × 24 = 47,696.40 rubles.
3. Let's calculate the amount of severance pay. To determine the size of this financial cushion during layoffs, you need to multiply the average daily income by the number of working days for which OyTV LLC must pay Ilya. The company must pay for the month from 07/12/14 to 08/11/2014. 21 actual working days fall within this period.
Kubikov’s earnings per day, which will be used in this calculation, are equal to:
617,431.37 rubles of annual payments / 215 working days = 2,871.77 rubles per shift.
Let's multiply the average daily earnings by working days in the period paid by severance pay in case of layoffs, and we get the amount that OyTv should accrue to the employee: 60,307.17 rubles.
4. Let's calculate the amount of average earnings for the period of employment. Since we know that Ilya Kubikov registered with the employment service, but could not find a new job within two months, he should be paid severance pay for the second month. In the period between July 12 and September 11, 2014, there are 44 days for work, so OyTv LLC will have to give the employee funds in the amount of: 44 × 2,871.77 rubles = 126,357.88 rubles. For the first month, Ilya was paid 60,307.17 rubles at once, so in September it remains to transfer him the difference of 66,050.71 rubles.
If in the third month Kubikov cannot find a job in another company, then the employer will have to pay for another 21 working days (from 12.09 to 11.10). This is an additional benefit in the amount of 60,307.17 rubles.
Is severance pay subject to personal income tax reduction?
All funds issued to an employee after a layoff are reflected in and are administered by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and are regulated by laws on social and pension insurance and on accidents in the workplace. Severance pay during layoffs is also governed by orders of ministries and the Government of the Russian Federation.
What taxes are subject to? No severance payments for reduction or dismissal at the initiative of the employee are subject to taxation. A citizen, losing his place of employment, receives financial support without deducting personal income tax, insurance contributions, etc. This norm is spelled out in Articles 217 and 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
However, there is one amendment: taxes are not withheld from those severance payments that do not exceed three months’ earnings (and for workers in the Far North - the average six-month income of the dismissed person).
On the other hand, although personal income tax and insurance premiums are not withheld from severance pay during layoffs, this payment is important when calculating the company’s income tax. For individual entrepreneurship, this is recorded in the “Other income” section (code 4800).
Basic wiring. Payment of severance pay is made on the basis of an order from the director of the company to lay off an employee due to staff reduction. The amount of such compensation is noted in the accounting reports as labor costs. This is regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (see Article 255).
If we turn to KOSGU, then in subparagraph 262 we will see the costs of severance pay when reducing: “Social assistance benefits to the population.” They are also recorded in the following posting: credit 0.302.62.30 and debit 0.401.20.262, which is marked in the documentation as “Accrual of severance pay.”
These funds, received by a citizen when staffing is reduced, act as a financial cushion and assistance in the near future, when he risks being left without the previous source of income and not finding a new one. Severance pay in case of layoff is not subject to personal income tax and leaves the opportunity to look for another job that will suit the candidate.
At the same time, the principle “what goes around comes around” turns out to be significant, since the amount of “compensation” is directly proportional to the time of work and its quality, because it is tied to the average daily income and length of service in the company.
- Dismissal of an employee at the initiative of the employer: how to avoid the revenge of an offended employee
When should severance pay be paid in case of staff reduction?
An employee who has been laid off is not always immediately given all the money required. Therefore, let’s look at what mandatory payments should be made and when:
On the day of dismissal, the worker has the right to expect a final payment from the company (this is regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Articles 140, 178 and 318). It includes:
- salary for days worked;
- money for unused vacations;
- severance pay for layoffs for one month.
When the first month passes after the layoff, the employing company does not owe the former employee anything. But after the next 30 days, the citizen has the right to another payment of the average monthly income. To do this, he must present to management an application and a work book without new entries. This procedure is established by part 1 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Severance pay for the second month in the event of a layoff is not paid in full and is recalculated if the person is employed in the middle of this month. Then the accounting department calculates an amount proportional to the days on which he has not yet worked.
At the end of the third month. Part 2 of Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that there are two situations in which the employer must pay for the third month after layoff:
- The employee came to the employment center in the 14 days following his dismissal and registered there.
- The employment service was unable to provide the citizen with work in the next three months after dismissal and issuance of severance pay for layoffs.
If this is the situation and the dismissed employee was unable to find a new source of income, then the employment center will issue a document that will serve as the basis for the former employer to issue average income for the third month.