Forms of entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurial activity: essence, forms and current development trends in Russia Collective entrepreneurship is carried out by a group of citizens on the basis
Lesson #2
Topic: Organizational and legal forms of entrepreneurship
- Resources and factors of production.
- Types of business activities.
- Organizational and legal forms of entrepreneurial de-
activities (private enterprise, partnerships, societies,
corporations, etc.) - Didactic game “Profitable Idea”.
Lesson objectives:
- To familiarize students with the main types and forms of enterprise
care in Russia. - Cultivate entrepreneurship.
- Develop the skill of economic analysis.
Teaching methods: Story, conversation, explanation, demonstration, self-
independent work, didactic game.
Equipment: Diagrams, posters, game equipment.
Interdisciplinary connections: technology, social studies
During the classes:
I. Organizational moment.
Greeting, checking the payroll, preparing for the lesson.
P. Checking homework.
Sh. Updating.
Students are asked to ask a number of questions:
- What are factors of production?
- What types of business activities do you know?
- What forms of entrepreneurship do you know?
IV. Explanation of new material.
1) An entrepreneur, as already mentioned, relying on his own
activity, establishes the production of goods or services. For anyone
production in any economic formation is necessary
resources. Resources are a set of natural, material,
financial, social and spiritual forces that can be used
called into the production process to create goods and services.
All resources are divided into natural, material, labor
high and financial.
Natural, material and labor resources are resources
without which no production can exist, therefore
they got the name basic
. Financial resources arising
in market conditions, received the name derivatives
. What then does it mean?
do they expect “factors of production”? What is their difference from “production resources”?
leadership"?
When characterizing production resources, we note that they are
everything that can be involved in the production process, and factors
production denote the resources actually involved in the process
production. Consequently, “production resources” are broader
a different concept than “factors of production”. Unlike resources,
factors become such only in the production process, mutually
interacting with each other. Therefore, production is always mutual
action of factors.
Factors
- this is what is used in the production process
and what directly determines the progress of production and its results.
These include: natural resources (land and natural resources);
production resources (buildings, equipment, machines, etc.);
labor resources (people, their physical and mental abilities).
In a market system, economists identify a fourth factor of production:
leadership - entrepreneurial ability. Businessman takes
took the initiative to connect natural, industrial and labor
commercial resources into a single process of production of goods or services.
2) There are several types of business activities:
- production,
- commercial (trading),
- financial,
- insurance,
- mediation.
Manufacturing Entrepreneurship
characterized by
that the entrepreneur and his company work in the field of direct
production of goods and services, selling which they make a profit.
In the field commercial entrepreneurship
entrepreneur
acts as a merchant, selling finished goods to the buyer,
acquired by him from others. Profit is made through sales
goods at a price higher than the purchase price.
Financial Entrepreneurship
- a special form of commercial
entrepreneurship, in which, as the subject of sale and purchase
are money and securities. The entrepreneur's profit arose
It results from the sale of financial resources with interest charged
Mediation
- a specific type of entrepreneurial
activity, closely adjacent to other types, it is co-
an integral part of production, financial and commercial
entrepreneurship. The intermediary stands between the manufacturer
or the seller on one side and the buyer on the other, connecting
them into one chain of business transactions. Object of purchase and sale
live is the information that the intermediary receives from the manufacturer
body (seller) and transfers it to the buyer. For the so-called service
he receives remuneration as agreed or established
standards
Insurance business
- here you are an entrepreneur
acts as a seller of insurance services, offers personally or
through intermediaries - insurance agents - to purchase services of potential
new buyer. Object of business activity
becomes an insurance service that is sold for a certain fee.
It should be noted that all types of entrepreneurial activities
activities are interconnected, so that when you engage in one activity, you will inevitably
le have to deal with other species.
3) There are several forms of private entrepreneurship.
According to the type of property they are divided into individual and number
lective
. To individual forms of entrepreneurial de-
activities include:
- individual work activity,
- sole proprietorship and
- family business.
Self-employment activity
carried out without pre-
changes in hired labor. Carried out using hired
labor, it is registered as a sole proprietorship.
Family business
differs in that the funds for activities
The assets of the enterprise are formed from the assets of the family and all family members
are the owners of the enterprise, profits are distributed in
depending on participation in the activity or previously agreed purposes.
Advantages of a custom form:
- complete independence;
- efficiency of management and decision-making;
- direct and immediate incentive for effective activities
ness of the enterprise; - maximum incentives, etc.
Flaws:
- difficulty in attracting large capital;
- uncertainty of terms of activity;
- unlimited liability for debts;
- a sole owner cannot be an expert in all matters
production dew; supply, sales, etc., which leads to
making wrong decisions.
Collective form
entrepreneurship is carried out
group of citizens based on their own property and various
forms of attracting property of other individuals. It includes-
xia: companies, partnerships, corporations, joint-stock companies, etc.
According to the nature of economic relations of society, there are two types:
with limited and unlimited liability.
Additional liability company
– pre-shape
entrepreneurial activity, in which all members of the team are not
days unlimited joint and several liability for obligations
the company with all its property. This means that it is not necessary to
to give the members of the collective equal parts of the capital and distribute equally
well, income, but in case of failure, each of them is responsible
not only in proportion to its share, but also covers the losses of others
partners.
Limited Liability Company
- this is an established
a business company established by one or more persons, chartered
whose capital is divided into shares, the sizes of which are determined
constituent documents; members of the company do not respond to it
obligations and bear the risk of losses associated with the activities
society, with their contributions.
Partnerships
is an association of several persons for a joint
commercial activities, but not capital. There are complete
(open) partnership and limited partnership.
General partnership
assumes that each partner participates
participates in the affairs of the partnership and bears full responsibility for the obligations
transactions not only with invested capital, but also with all property.
Limited partnership
– an association consisting of half-
nal comrades who are responsible only within the limits of their
contribution (limited partners).
Advantages of partnerships:
- easy to organize;
- economic (material, labor, financial) opportunities
ness increases; - there is an opportunity to attract qualified
nal specialists;
Flaws:
- limited financial resources;
- ambiguous understanding of the goals of the activity;
- unlimited liability of partners not only for their own
own decisions, but also for the consequences of the actions of others; - the difficulty of determining the measure of each in the income or loss of a company
we, division of property; - unpredictability due to the exit of one person from the company
of her partners;
Corporation
is a legal form of business created for joint
conducting business activities by combining capital
for the purpose of making a profit.
Joint-Stock Company
is a company whose authorized capital
Rogo is divided into a certain number of parts (shares) equal to
minimum value. There are two types of joint stock companies:
open and closed.
Open joint stock company
called society
whose participants can freely sell and buy shares
company without the consent of other shareholders.
Closed joint stock company
– promotions are distributed
only among the founders (among a predetermined circle of people).
Advantages:
- members of the company have limited liability;
- the procedure for buying and selling a participation interest (shares) is simple;
- this form is more effective for attracting additional
private capital for the development of production, i.e. you can take out a loan.
Flaws:
- establishing a joint stock company is a complex and time-consuming matter;
- is subject to double taxation (firstly,
as an independent legal entity pays tax on profits; secondly, part of the profit distributed among shareholders
as a dividend, is taxed again as personal income.
citizens' moves); - difficulty in making a single decision.
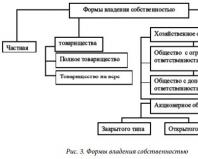
Each business form has its own advantages
and disadvantages (see Table 9) therefore, when opening your own business,
Bodies themselves choose one or another form of activity, guided by
personal interests. Property ownership forms shown
in Fig. 3.

I. Practical work: Didactic game “Profitable Idea”
(see Appendix 5).
II. Homework: continue filling out the table. 9.
Create a crossword puzzle on the topic “Entrepreneurship.” Choose
and justify the organizational and legal form of your enterprise.
III. Summing up the lesson, grading.
A collective type of business involves conducting it jointly by several persons. Individual entrepreneurs, as the name suggests, act independently, make decisions and carry out activities at their own peril and risk. The individual entrepreneur is liable for personal property that he owns by right of ownership. Collective entrepreneurship implies common property, each member contributing his share to the common business. Accordingly, obligations also imply general responsibility for their implementation.
Collective entrepreneurs
Collective and individual entrepreneurs perform the same functions in the business process. But there are still some differences. Collective business entities include:
- Business societies and partnerships. They can carry out the same business as individual entrepreneurs, namely: organize insurance companies, act as intermediaries, produce and sell products, etc. According to the definition of the Civil Code, the contributions of each of the founders form joint property, that is, the authorized capital. Materials and products, both finished and manufactured, belong to the entire membership of the society.
- A production cooperative can also be classified as collective entrepreneurship. The number of its participants must be more than five people. The main composition of a cooperative is an individual entrepreneur, that is, an individual, but it is also permissible for legal entities to participate in the cooperative. Participants make a share contribution - cash, securities, property rights and the property itself. Members can take a personal part in the functioning of the cooperative, or they can be part of it without carrying out labor activities within the framework of this cooperative. The number of the latter persons should not be more than 25% of the total composition of the entire cooperative. The cooperative's assets are represented by contributions from its members. A cooperative, like legal entities, has a charter. If the cooperative has more than 10 members, you can elect a board, and if more than 50 - a supervisory board.
- A holding is an actual association of several enterprises, the shares of which must include securities of several legal entities. On the territory of the Russian Federation, mainly closed joint-stock companies are created under the name of a holding, and the holding itself may not be an independent company, but a subsidiary of another holding. Enterprises are also united into trusts, syndicates, cartels, consortiums and conglomerates. All these societies are based on the pooling of property - capital, securities and other things - temporary or permanent.
The most common form of doing business in collective entrepreneurship is management. Such companies are most convenient in terms of registration, adaptation to constantly changing market conditions, and the liability for obligations of its members is not excessive.
Individual entrepreneurship
Collective and individual entrepreneurs carry out their activities after mandatory registration. This procedure is carried out by the Federal Tax Service. An applicant for individual entrepreneur status submits an application, personal documents and pays a state fee. After receiving the registration certificate, you must register with the Pension Fund, and if the entrepreneur plans to hire staff, with the Social Insurance Fund and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund. An individual entrepreneur can also voluntarily pay contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for himself. When choosing the type of future business, the individual entrepreneur indicates OKVED codes, thereby determining the direction of his economic activity. However, some types of businesses require the acquisition of a license or permit to operate them. Information about individual entrepreneurs is entered into the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs. Registration of collective business companies also occurs in the tax structure. Information about legal entities that are part of collective entrepreneurship entities is entered into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
We must remember that an individual entrepreneur bears much greater responsibility compared to a collective form of doing business. The personal property of the individual entrepreneur is the object of repayment of the obligations that have arisen, while collective entrepreneurs share this responsibility among themselves. Also, some entrepreneurs, especially new ones, find it quite difficult to make business decisions alone. Discussing important points at a meeting of members of a collective society makes their adoption more effective and efficient.
A form of entrepreneurship is a system of norms that determines the internal relations between partners in an enterprise, on the one hand, and the relations of this enterprise with other enterprises and government bodies, on the other.
There are the following main forms of entrepreneurship:
- 1. individual entrepreneurship;
- 2. collective entrepreneurship.
Individual entrepreneurship is understood as systematic activity, independently carried out, in one’s own name, under one’s own responsibility, with the aim of making a profit and under the conditions established by this law. An individual entrepreneur is an individual (citizen) who personally conducts business on his own behalf, at his own expense and at his own risk, and independently makes business decisions. An individual entrepreneur bears personal full responsibility for the results of his activities. This means that in the event of debt formation, the entrepreneur pays with all his property. At the same time, the entrepreneur works himself, without attracting additional labor. Such entrepreneurship is classified as self-employed and registered with local authorities, carried out on the basis of a patent, and the entrepreneur pays taxes as an individual.
An individual entrepreneur can use his own property and, under an agreement, the property of other persons in business activities. He can borrow money, get a loan from banks, other organizations or individuals. An individual entrepreneur independently distributes the profit from his activities remaining after taxes. Individual entrepreneurship is based on private property and most often has the character of a small business. In this capacity, individual entrepreneurship contributes to the demonopolization of the economy and strengthens competitive principles. It makes the economy more flexible, capable of rapid self-regulation. But it is difficult to attract large capital to individual entrepreneurship due to lower creditworthiness compared to collective forms of entrepreneurial activity. Since an individual business is based on the entrepreneurship of one person, it is profitable while the businessman is active, and the life of such an enterprise is uncertain, so creditors are not always willing to enter into long-term financial transactions with an individual entrepreneur. Individual entrepreneurship is characterized by a high level of risk and a lack of specialized management. Typically, an entrepreneur is the owner and performs all functions of enterprise management (production, supply, sales, finance), which requires universal knowledge in many areas of production. The lack of financial resources and the inability to attract specialist managers to management leads to the adoption of suboptimal decisions. Individual entrepreneurship requires more significant and real support from the state. Collective entrepreneurship (partnership) is a form of organization of entrepreneurial activity in which two or more entrepreneurs make joint decisions and bear personal property responsibility for running the business. At the end of the 20th century. collective forms of entrepreneurship have taken a dominant position in both small and large-scale businesses.
Collective entrepreneurship, in turn, is divided into:
- - full partnership;
- - partnership of faith;
- -limited liability company;
- -company with additional liability;
- -closed joint stock company;
- -public corporation.
A general partnership is a type of business partnership, the participants of which (general partners), in accordance with the agreement concluded between them, are engaged in entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership and are liable for its obligations not only in the amount of contributions to the share capital, but with all the property belonging to them, that is, “full ", unlimited liability. Limited partnership (mixed partnership) is an association in which, in accordance with the constituent agreement on the creation of the partnership, one or more of its full members bear full (unlimited) liability for the obligations of the partnership with all their property, and the remaining contributing members bear liability associated with activities of the partnership, within the limits of their share of the capital of the partnership, including the unpaid part of their contribution. A mixed partnership, like a general partnership, can be created without establishing a new legal entity - in this case, the contributions of the participants of the partnership are reflected on the balance sheet of one of the full members of the partnership; with the establishment of a new legal entity and with separate property - in this case, the contributions of the participants are reflected on the balance sheet of the partnership.
Representation and actions on behalf of a full or mixed partnership of any of its active members are recognized as the activities of the partnership itself, unless otherwise provided by the constituent documents of the partnership. Another type of collective business that involves limited economic liability is a limited liability company. It is an enterprise that has an authorized capital divided into shares, the size of which is determined by the constituent documents. Participants in a company can be both individuals and legal entities, and participants in the company are liable for its obligations only to the extent of their contributions. Much in the structure of a limited liability company resembles a joint stock company, but there are also serious differences:
- - a limited liability company is a necessarily closed enterprise;
- - creating a joint stock company requires more effort than a limited liability company.
According to Russian legislation, the number of participants in such a company should not exceed the limit established for this type of business association; otherwise, within a year it is subject to transformation into a joint-stock company. In addition, 000 cannot have another business company consisting of one person as its sole participant. Company with additional liability. The participants of such a company, unlike a limited liability company, are liable for its debts with their contributions to the authorized fund, and if these amounts are insufficient, with additional property belonging to them in the same multiple of the contribution of each participant for all participants. The maximum amount of liability is provided for in the constituent documents. An additional liability company is a business company established by one or more persons, the authorized capital of which is divided into shares of the size determined by the constituent documents. Participants in an ALC jointly and severally bear subsidiary liability for its obligations with their property in the same multiple of the value of their contributions, determined by the constituent documents of the company. In the event of bankruptcy of one of the participants, his liability for the obligations of the company is distributed among the remaining participants in proportion to their contributions, unless a different procedure for the distribution of liability is provided for by the constituent documents of the company. A classic joint-stock company (corporation) is an association of capital investors (shareholders), formed on the basis of the charter and having an authorized fund, divided into a certain number of shares of equal par value, the founders of which can be both individuals and legal entities. The company must consist of at least two participants, and their maximum number is not limited. Joint-stock companies are the most democratic form of business, because anyone can buy shares and become a shareholder (and thereby the owner) of an enterprise with an open signature for the shares. In world practice, of course, there is also a closed subscription for shares, which is used, as a rule, in the case when the founders of a joint-stock company have sufficient funds to fully form the authorized capital of the enterprise. Main features of the joint-stock form of the enterprise:
- -shareholders are not responsible for the company’s obligations to its creditors, the company’s property is completely separate from the property of individual shareholders. In case of insolvency of the company, shareholders bear only the risk of possible depreciation of the shares they own;
- -the joint-stock form of an enterprise makes it possible to unite an almost unlimited number of investors, including small ones, and at the same time maintain control of large investors over the activities of the enterprise;
- -a joint stock company is the most stable form of capital consolidation, since the departure of any of the investors from it does not entail the mandatory closure of the enterprise.
The limitation of risk to a predetermined amount makes a joint stock company the most attractive form of investment and, as a consequence, provides an opportunity to centralize large amounts of funds. It can be said that the issue of shares is one of the most significant achievements of a market economy. This is a way to mobilize resources, a way to “disperse” risk and a way to instantly transfer funds from one industry to another. Thus, there are 2 main forms of entrepreneurship: individual and collective, which in turn are classified into large, medium and small. Collective entrepreneurship received special development in the 20th century. and currently occupies a dominant position in both small and large scale businesses. It can exist in various forms.
Collective entrepreneurship is represented by various cooperatives. Very often there are industrial ones, when several people unite of their own free will in order to further carry out some activity. It can be industrial or economic. Important features are personal participation, the presence of shares that are combined.
general information
Collective entrepreneurship is carried out by a group of citizens based on the individual interests of each participant. At the same time, all interested parties work together, combining their efforts. This imposes considerable restrictions, because responsibility for entrepreneurship is directly related to the property owned by all participants in the business. Responsibility for fulfilling their obligations falls on everyone.
When conducting business, such a legal entity performs standard functions that are in many ways similar to individual entrepreneurship.
Classification
In modern economics, it is customary to divide collective entrepreneurship into subtypes. This:
- partnerships, societies;
- production cooperatives;
- holdings;
- management.
First things first: partnerships and economic entities
What are collective forms of entrepreneurship in this category? Various companies:
- insurance business;
- mediation;
- sale;
- production of goods.
Feature: each founder invests his own property, which in total forms joint property. It is this that serves as the authorized capital. All products and goods used in the work process, as well as finished ones, are in the possession of all members of such a community.

Production cooperative
The comparative characteristics of individual and collective entrepreneurship are most clear when studying this particular subtype. And the whole point is that in the case of an individual business, as the name already implies, the organizer is just one activist who wanted to try his hand. But a production cooperative can only be opened when there are at least five interested parties who are ready to join forces. Individual entrepreneurs, individuals, and legal entities can act as creators of PCs.
When considering the signs of collective entrepreneurship, the first thing to note is the share contribution. This is how it is customary to designate the property that is contributed by each participant. It can be:
- money directly;
- securities;
- property rights;
- property.
Each member has an impact on how the company as a whole will operate. It is also permissible for members of a cooperative not to participate in labor activities. But not everyone can do this, but only a quarter of the total composition of society.
The asset of a production cooperative is only as great as its members have invested in it. The development of a charter is mandatory. If the number of members exceeds ten, the creation of a cooperative board is allowed. You can form a supervisory board when there are more than fifty members of the community.

Holding
In this form, collective entrepreneurship is carried out by a group of citizens on the basis of several pre-existing enterprises that have undergone merger. In this case, the shares must contain securities of various legal entities.
In Russia, holdings mainly become closed joint stock companies. At the same time, it is not necessary for the holding to be independent; it can be a subsidiary of, for example, a larger holding.
It is also worth remembering that a holding is not the only possible format for combining enterprises into a single whole. Relevant forms of collective entrepreneurship:
- syndicates;
- cartels;
- trusts;
- conglomerates.
Regardless of the specific type, the common thing is that the values and capital of all legal entities are combined. In some cases the phenomenon is temporary, in others it becomes a permanent solution.

Management
Analyzing individual and collective entrepreneurship in Russia today, we can safely say that it is business management that leads in popularity. This is not surprising, because registering a company is simple and requires little time and money. At the same time, the company will be flexible and will easily adapt to the constantly changing realities of the market. Another important positive feature of this form of doing business is the relatively small personal responsibility of each of the members who organized the enterprise.
Partnerships
If you look at individual and collective forms of entrepreneurship, you will notice that a general partnership looks quite attractive. Its participants, as the name suggests, are full comrades.

The specificity of the work of this format is that it all begins with the conclusion of an agreement between members of the community, which must strictly describe all business activities planned by the organization.
Also attracting attention are such types of collective entrepreneurship as partnerships of faith and various societies. The first assumes that there are participants who work on behalf of the organization. It is they who will be liable with property for all obligations assumed by the company. In addition, there are several investors who risk losses if something goes wrong. In this case, the amount of loss cannot be greater than what the investor invested in the business. Such limited partners cannot conduct direct business activities.

Collective entrepreneurship: societies
First of all, the limited liability company deserves mention. This is the customary name for a form of entrepreneurship in which there is one or several founders. There is also a share capital divided into parts. The division is carried out in accordance with the constituent documentation. A distinctive feature of this format is the absence of liability for the obligations of a legal entity on each of the participants. There is a certain risk of losing the invested money, but no more than the amount that the participant contributed to the “common pot”.
There is another type of company, it is called “with additional liability”. His example clearly shows how the characteristics of individual and collective entrepreneurship differ. An enterprise is founded either by one person or by several, but is nonetheless collective. It has an authorized capital divisible by shares. Each of the participants, together with others, is responsible for the obligations of the event. And here the amount is not limited only to that contributed to the authorized capital.
Finally, a joint stock company is a form of activity when a group of individuals opens their own business and collects authorized capital for this, dividing it into shares. Shareholders, as all participants in this business are usually called, are not liable for the obligations of the enterprise, and can only lose what they invested when receiving the shares.
In some cases, this form of activity is closed, in which case only the founders, as well as a strictly limited circle of persons, have access to the shares. But in the case of an open format, shares can be alienated without asking the consent of other participants in the company.

The most common
When considering collective entrepreneurship, one cannot help but pay special attention to the production cooperative. This form is very common. It occurs when people unite voluntarily. Each of them becomes a member of a formed society in order to conduct production and economic activities together. Each member participates through a share contribution and his own labor, taking a personal part in the work of the company. An enterprise formed in this way must be registered as a legal entity.
As a rule, the main purpose of such an enterprise is the production of some goods, the processing of products or their sale, as well as construction and provision of services. In some cases, companies are created for the purpose of:
- extraction of natural resources;
- working with recyclable materials;
- research;
- design;
- scientific works;
- provision of services.
A very large group of collective entrepreneurship in this category are agricultural organizations, fishing organizations, and cooperative farms.
Some features
To establish a production cooperative, you must have at least five interested parties. Each of them must make their contribution. The participation of persons who do not have citizenship at all, as well as those who are citizens of other countries, is allowed. The charter of the enterprise describes the conditions under which the company cooperates with other legal entities. The company may employ hired employees, but their number may not exceed 30% of the number of people making up the cooperative.

It is allowed to have those people who have made their contribution, but do not take any part in the activities of the company. There may be no more than a quarter of all those who made contributions. If we are talking about agriculture, then such membership, when a person does not actually participate in the work, is usually called associate. Most often this belongs to legal entities. In addition, there are also citizens who:
- retired;
- cannot work due to health reasons;
- were selected for some position outside the collective enterprise;
- employees in the RF Armed Forces;
- fall under the points specified in the charter of the enterprise.
The charter is the only constituent document for such a business. It is approved as part of a meeting of all members. In order for the cooperative to receive property at its disposal, its members make contributions based on the requirements of the charter. Additionally, property is formed by the profitability of the business.
Zero fund is a term applied to a situation where property is present in a minimum amount sufficient to cover the interests of creditors. Shares are those parts into which the common property of the cooperative is divided.
Company management
If a production cooperative grows and has at least fifty people on its staff, it is possible to create a rather complex management structure. If at first it was only a general meeting of all members, then if the number of members exceeds 50 people, a supervisory board can be organized. This is an optional phenomenon, but practice shows that it structures the work process and also allows you to keep the situation under control.
The executive body is the chairman and the board headed by him.

The general meeting can then make a decision that affects the work of the organization as a whole when at least half of the number has attended. If we are talking about agriculture, then the indicators are decreasing; the presence of a quarter is enough. Special conditions apply to agricultural production cooperatives with fewer than 20 people. Here it is necessary that at least five people take part in the council.
Summing up
Structuring all of the above, we will highlight all possible collective activities:
- partnership, partnership;
- economic community;
- production cooperative.
It is not surprising that it is cooperative forms that have become the most powerful in the world of business, because since ancient times it has been known that “there is no man in the field.” By pooling their resources, capabilities, and strengths together, several activists have the opportunity to achieve much greater success.
At the same time, collective entrepreneurship does not at all exclude private property. If you decide to create your own company, then register as a legal entity and join a collective enterprise. In this case, the individual entrepreneur retains his rights, but joins forces with other persons, which provides more opportunities to achieve goals. So that all participants can trust each other, so that everyone is confident that those around them are doing things only for the benefit of the company, it is necessary to create the correct charter and conclude a general agreement.

Shareholder ownership is another great opportunity to join a team but retain your individuality. Well, then it is possible to combine into even larger forms. You can organize syndicates and corporations. In short, the possibilities are endless.
In the organization of entrepreneurial activity, a special place belongs to partnerships - collective entities carrying out business operations. These include limited and unlimited liability companies, limited and joint stock companies, and some others. Each form of business requires a certain structure of interaction between partners and the size of the enterprise.
The activities of collective forms of entrepreneurship are regulated by the following regulations: Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ “On Joint-Stock Companies”; Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated 02/08/98. No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies”; Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated July 19, 1998. No. 115-FZ “On the peculiarities of the legal status of joint-stock companies of workers (national enterprises).”
Partnerships and societies
Business partnerships and companies are recognized as commercial organizations with an authorized capital divided into contributions of participants, which as their main goal pursue making a profit by carrying out any types of activities not prohibited by law.
Participants in companies and partnerships have the right to receive information about the activities of these organizations and bear obligations to make contributions to the authorized capital and non-disclosure of information constituting a trade secret (Part 2 of Article 67 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The main difference between companies and partnerships is that the former are an association of capital, i.e. the participation of the founders is expressed primarily in property contributions and not necessarily in personal labor, and the latter are an association of persons, because founders, as a rule, not only participate in the activities of the partnership with their property, but are also directly engaged in entrepreneurship.
Another significant difference is that participants in companies bear only the risk of losses within the limits of their contribution to the authorized capital, and participants in partnerships bear limited liability for debts within the limits of all property (this rule does not apply to investors in limited partnerships).
Finally, a business company, unlike partnerships, can be created by one founder, who becomes its sole participant.
Property created from the contributions of participants, as well as produced and acquired by a business partnership or company in the course of its activities, belongs to it as property.
State bodies and local government bodies do not have the right to act as participants in business companies and investors in limited partnerships, unless otherwise provided by law.
Owner-financed institutions may be participants in business companies and investors in partnerships with the permission of the owner, unless otherwise provided by law.
The law may prohibit or limit the participation of certain categories of citizens in business partnerships or companies, with the exception of open joint-stock companies.
Business partnerships and companies may be founders (participants) of other business partnerships and companies, with the exception of cases provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and other laws.
Contributions to the property of a business partnership or company can be money, securities, other things or property rights or other rights that have a monetary value.
Business partnerships, as well as limited liability and additional liability companies are not entitled to issue shares.
According to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, business partnerships are divided into general partnerships and limited partnerships.
General partnerships
Full A partnership is recognized, the participants of which (general partners), in accordance with the agreement concluded between them, are engaged in entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership and are liable for its obligations with the property belonging to them.
The business name of a general partnership must contain either the names of all its participants and the words “general partnership,” or the name (title) of one or more participants with the addition of the words “and company” or “general partnership.”
A general partnership is created and operates on the basis of a constituent agreement, which must be signed by all its participants. Management of the activities of a general partnership is carried out by general agreement of all participants. The founding agreement of a partnership may provide for cases when a decision is made by a majority vote of the participants. Each participant in a general partnership has one vote, unless the constituent agreement provides for a different procedure for determining the number of votes of its participants.
Profits and losses of a general partnership are distributed among its participants in proportion to their shares in the share capital, unless otherwise provided by the constituent or other agreement of the participants.
An agreement to exclude any of the partnership participants from participating in profits or losses is not permitted.
Features of a general partnership:
- v The entrepreneurial activity of its participants is recognized as the activity of the partnership itself as a legal entity.
- v If there is insufficient property of the partnership to pay off its debts, creditors have the right to demand satisfaction from the personal property of any of the participants (or all of them together). Therefore, the activities of the partnership are based on the personal trust relationships of all its participants, the loss or change of which entails the termination of the activities of the partnership. Commercial practice shows that such partnerships often become a form of family entrepreneurship.
- v Any of the participants in a general partnership is engaged in business activities on behalf of the partnership as a whole, therefore, for the creation and functioning of a general partnership, a charter establishing the competence of its bodies is not required. The only constituent document of such a commercial organization is the constituent agreement.
Partnership of Faith
(limited partnership)
A limited partnership is a type of general partnership and is characterized by the following features.
- v A limited partnership consists of two groups of participants - general partners and investors. General partners carry out entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership itself and bear unlimited and joint liability for obligatory partnerships. Another group of participants - investors (command partners) - only make contributions to the property of the partnership, but are not liable with their personal property for its obligations. Thus, in a limited partnership it is allowed to use the capital of third parties (investors), i.e. it becomes possible to raise additional funds not at the expense of the property of general partners, which is their advantage compared to general partnerships.
- v The inclusion of the investor’s name in the business name of a limited partnership automatically leads to his transformation into a full partner, primarily in the sense of unlimited and joint liability with his personal property for the debts of the partnership.
- v The law specifically regulates the legal position of the investor in a limited partnership. The investor does not have the right to participate in the management of the affairs of the limited partnership and act on its behalf, but they have the right to get acquainted with the financial activities of the partnership.
- v Investors in a limited partnership have three property rights related to their contribution to the property of the partnership: the right to receive their share of the partnership’s profits; investors retain the opportunity to freely withdraw from the partnership with the receipt of their contribution; the investor can transfer his share or part thereof either to another investor or to a third party, and the consent of the partnership or general partners is not required.
- v When a limited partnership is liquidated, investors have a priority right over general partners to receive their contributions or their cash equivalent from the property of the partnership after satisfying the claims of other creditors.
Advantages of a general partnership:
- v The ability to accumulate significant funds in a relatively short period of time.
- v Each member of a general partnership has the right to engage in business activities on behalf of the partnership on an equal basis with others.
- v General partnerships are more attractive to creditors because their members bear unlimited liability for the obligations of the partnership.
Disadvantages: there must be a special trusting relationship between general partners, otherwise the collapse of this organization may quickly occur; Each member of a general partnership bears full and joint unlimited liability for obligations, i.e. in the event of bankruptcy, each member is responsible not only with the contribution, but also with personal property.
General partnerships have the same advantages and disadvantages as general partnerships. Their additional advantage is that to increase their capital they can attract funds from investors; general partnerships do not have this opportunity.
Limited Liability Companies
Limited Liability Company (LLC) A company founded by one or more persons is recognized, the authorized capital of which is divided into shares of sizes determined by the constituent documents. Participants in a limited liability company are not liable for its obligations and do not bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the company, within the limits of the value of the contributions made by them.
The corporate name of a limited liability company must contain the name of the company and the words “limited liability”. The number of participants in a limited liability company must not exceed the limit established by the law on limited liability companies.
The constituent documents of an LLC are the constituent agreement signed by its founders and the charter approved by them. If a company is founded by one person, its constituent document is the charter.
The authorized capital of an LLC is made up of the value of the contributions of its participants and determines the minimum amount of the company's property that guarantees the interests of its creditors. The size of the authorized capital of the company cannot be less than the amount determined by the law on limited liability companies.
The supreme body of an LLC is the general meeting of its participants. The company may be voluntarily liquidated or reorganized into a specialized company or a production cooperative by unanimous decision of its participants.
A limited liability company has the following features:
- v It is a type of capital association that does not require the mandatory personal participation of its members in the affairs of the company;
- v Division of the authorized capital of the company into shares of participants and the absence of liability of the latter for the debts of the company;
- v The law provides for higher requirements for the authorized capital, its definition and formation, than for the share capital of the partnership. First of all, the size of this capital under no circumstances can be less than the minimum amount determined by law.
The advantages of LLC are as follows:
- v The ability to quickly accumulate significant funds;
- v LLC can be created by one person;
- v Members of the company bear limited liability for the obligations of the company.
Disadvantages: the authorized capital cannot be less than the amount established by law; LLCs are less attractive to lenders because members of the company bear only limited liability for the obligations of the company.
Additional liability company
Additional liability company (ALC) is essentially a type of limited liability company with all the general rules of such a company applied to it. Therefore, everything said about LLC applies equally to a company with additional responsibility.
The only important difference between these companies is that if the property of the company with additional liability is insufficient to satisfy the claims of its creditors, the participants of the company can be held to property liability, and jointly and severally. However, the amount of this liability is limited; it does not apply to all of their personal property, which is typical for general partnerships, but only to part of it - however, for all multiples of the size and amount of contributions made (for example, threefold, etc.). From this point of view, such a society occupies an intermediate place between societies and partnerships.
ODOs have the same advantages and disadvantages as LLCs. Their additional advantage is that they are more attractive to lenders because... bear additional personal responsibility for the obligations of the company, but at the same time this is also their disadvantage.